|
|
The Georges Bank region - located off the New England coast - has long supported important commercial fisheries. The objective of U.S. GLOBEC studies on Georges Bank is to understand how changes in environmental conditions related to stratification, retentive circulation features, and exchange across frontal zones affect the dynamics of the target copepod (Calanus finmarchicus and Pseudocalanus spp.) and fish (cod and haddock) species. Changes in growth and survival of the target fish species due to changes in food supply (including the target copepods) and the physical environment have important implications for recruitment to the fisheries for these valuable species ....
"Collectively, the Georges Bank studies have both enhanced our understanding of the ecology of the bank, and provided new tools for understanding fish population fluctuations and fishery management ...."
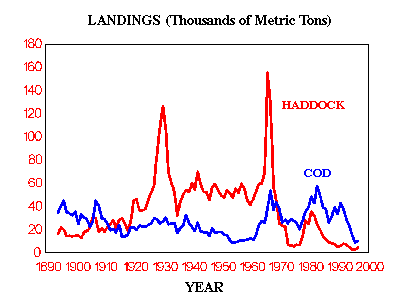 Commercial landings of Georges Bank cod and haddock .... |
As water temperatures increase during Spring on Georges Bank, a distinct layering develops. Warmer, fresher water accumulates at the surface, and colder, saltier water hugs the bottom along the outer bank. On the shallow central plateau of the bank, the water remains well mixed due to strong tidal currents, and nutrients are distributed throughout the water column. An important frontal zone develops on the bank between these well-mixed and stratified water masses that concentrates food such as small crustaceans (including the copepods, Calanus and Pseudocalanus) for cod and haddock larvae. Strong rotary tidal currents, coupled with stratification and the topography of the bank, result in a clockwise circulation pattern that can help retain the larvae ....
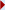
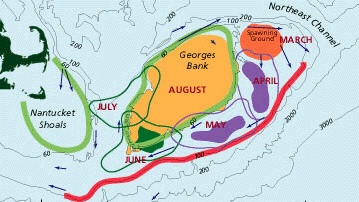 Cod and haddock spawn on the Northeast Peak of Georges Bank, and the eggs and larvae are carried by the clockwise currents around bank. The centers of distribution during different months are shown on this map. The red line shows the position of the shelf-slope front, and the green lines show the position of the tidal mixing fronts .... |
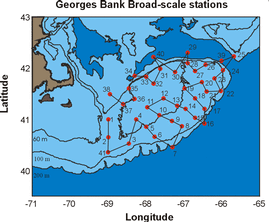 Location of broad-scale survey sampling locations on Georges Bank .... |
The U.S. GLOBEC Program has now completed a planned sequence of field studies on Georges Bank. Preliminary studies were initiated in 1993, and the first process-oriented studies were initiated in 1995 with studies of the role of stratification on the physical oceanography of the region and its implication for growth and mortality of larvae. The focus of process-oriented studies in 1997 was on physical factors affecting retention and loss of planktonic organisms on the bank. Finally, mechanisms of cross-frontal exchange were examined in 1999. Broad-scale observational studies were conducted in each year from 1994-99 at monthly intervals from January - June (the period of occurrence of cod and haddock eggs and larvae) to provide a broader context for interpretation of process studies. The Georges Bank program is now entering a final phase of synthesis and modeling activities in which the results of the various process, retrospective, and broad-scale studies will be integrated ....
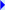
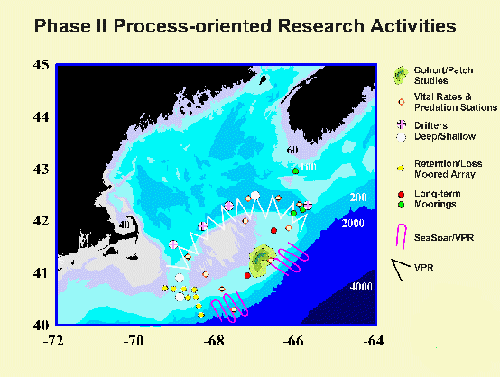 U.S. GLOBEC process-oriented studies are nested within the area of the broad-scale sampling program. An example of the location of process-oriented studies on Georges Bank during the 1997 experiments on mechanisms of retention and loss is illustrated above .... |
A number of important findings have already emerged that have substantially altered our views of the factors affecting oceanographic and ecological conditions on the bank. A potential signature of climate change related to ice conditions in the Arctic has been identified in changes in temperature and salinity on the bank during the GLOBEC study period. Episodic cross-overs of water from the Scotian Shelf to Georges Bank have been identified as potentially important events, with implications for exchange of planktonic organisms (including copepods, fish eggs, and larvae). The importance of a previously unsuspected predator related to jellyfish has been identified, and its potential impact on the target species is being investigated. Collectively, the Georges Bank studies have both enhanced our understanding of the ecology of the bank, and provided new tools for understanding fish population fluctuations and fishery management ....
|
An excellent general account of the GLOBEC Georges Bank program
appeared in the Quincy (MA) Patriot-Ledger in late December, 1997:
A New Understanding:Scientists are Recording the Weather, Currents, and Biology of the Georges Bank Fishing Grounds to Predict Future Stocks of Cod & Haddock by:Eric Niiler / Quincy (MA) Patriot-Ledger, 23 December, 1997 - Reprinted with permission |
[ Table of Contents ]
[ Top of Current Page ]
[ Advance to Next Section ]
 Georges Bank / NW Atlantic Program
Georges Bank / NW Atlantic Program


